LG – 机器学习 CV – 计算机视觉 CL – 计算与语言 AS – 音频与语音 RO – 机器人
转自爱可可爱生活
摘要:神经网络分布漂移性能预测、语言模型的理由增强集成、具有无分布可靠性保证的推荐系统、延时摄影序列随机与循环效应的解缠、基于隐式差分的迭代细化算法训练、生物机器人新兴跨学科领域综述、通过分布式优化实现多肢机器人自由攀爬同时接触丰富抓取与运动、坚固多功能四足自由攀爬机器人、标签和文本驱动的对象辐射场
1、[LG] Agreement-on-the-Line: Predicting the Performance of Neural Networks under Distribution Shift
C Baek, Y Jiang, A Raghunathan, Z Kolter
[CMU]
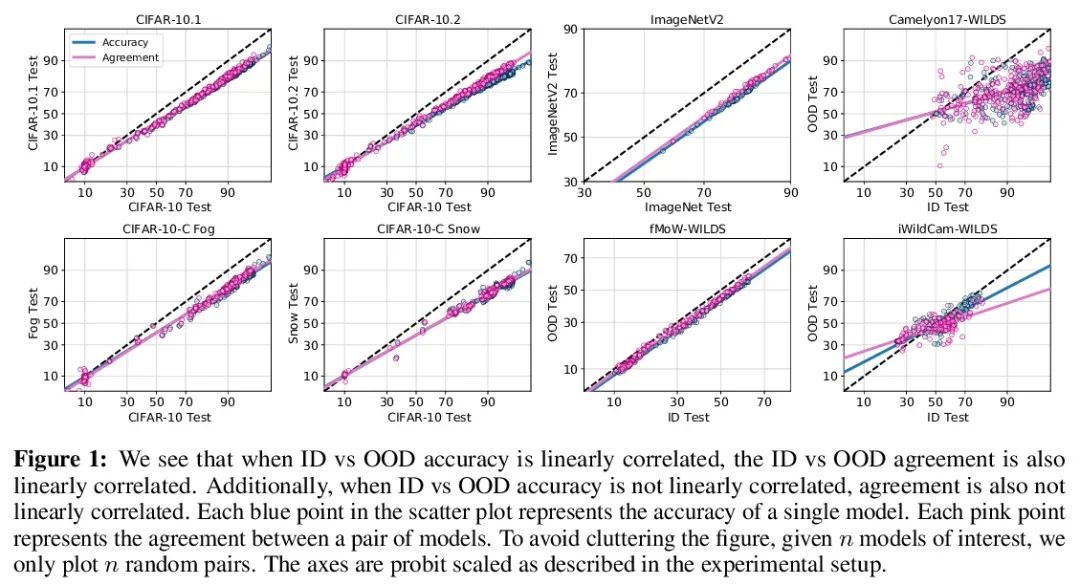
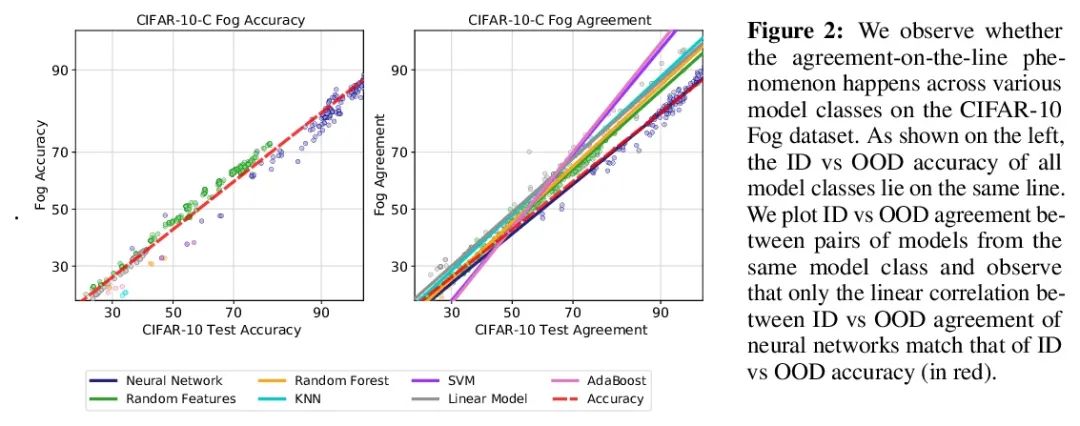
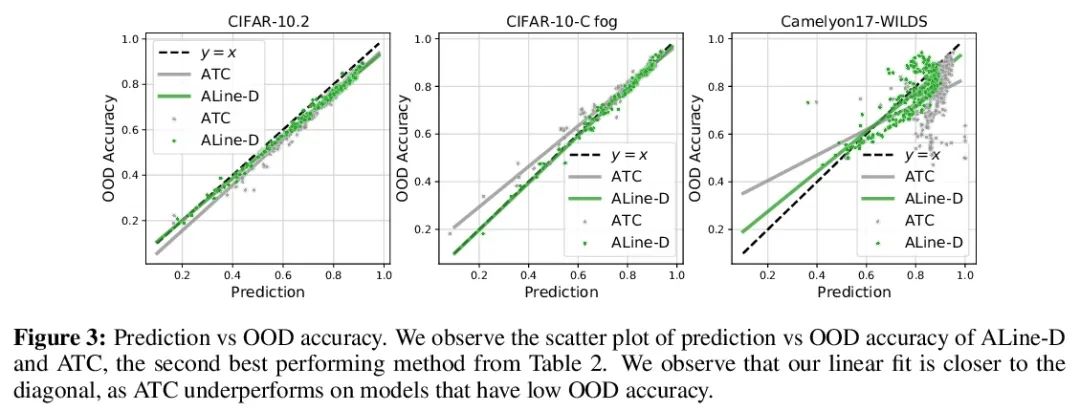
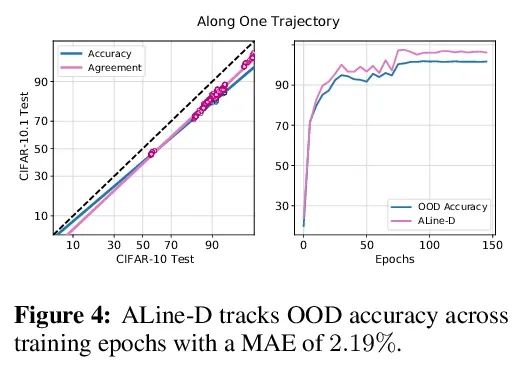
Agreement-on-the-Line:神经网络分布漂移性能预测。最近,Miller等人表明,一个模型的分布内(ID)精度与它在几个OOD基准上的分布外(OOD)精度有很强的线性相关性——他们把这种现象称为”线上精度(accuracy-on-the-line)”。虽然这是一种选择模型的有用工具(即最有可能表现出最佳OOD的模型是具有最高ID精度的模型),但这一事实并不能帮助估计模型的实际OOD性能,因为没有获得标注OOD验证集。本文展示了一种类似但令人惊讶的现象,即神经网络分类器对间的一致性也是成立的:无论accuracy-on-the-line是否成立,本文观察到任意两个神经网络(具有潜在的不同架构)预测间的OOD一致性也与它们的ID一致性有强烈的线性关系。此外,我们观察到,OOD vs ID的一致的斜率和偏差与OOD vs ID的精度密切相关。这种现象,称之为线上一致(agreement-on-the-line),具有重要的实际应用意义:在没有任何标注数据的情况下,可以预测分类器的OOD精度,因为OOD一致可以用未标注数据来估计。该预测算法在agreement-on-the-line成立的漂移中,以及令人惊讶的,在精度不在线上的情况下,都优于之前的方法。这一现象也为深度神经网络提供了新的见解:与accuracy-on-the-line不同,agreement-on-the-line似乎只对神经网络分类器成立。
Recently, Miller et al. [56] showed that a model’s in-distribution (ID) accuracy has a strong linear correlation with its out-of-distribution (OOD) accuracy on several OOD benchmarks — a phenomenon they dubbed “accuracy-on-the-line”. While a useful tool for model selection (i.e., the model most likely to perform the best OOD is the one with highest ID accuracy), this fact does not help estimate the actual OOD performance of models without access to a labeled OOD validation set. In this paper, we show a similar but surprising phenomenon also holds for the agreement between pairs of neural network classifiers: whenever accuracyon-the-line holds, we observe that the OOD agreement between the predictions of any two pairs of neural networks (with potentially different architectures) also observes a strong linear correlation with their ID agreement. Furthermore, we observe that the slope and bias of OOD vs ID agreement closely matches that of OOD vs ID accuracy. This phenomenon, which we call agreement-on-the-line, has important practical applications: without any labeled data, we can predict the OOD accuracy of classifiers, since OOD agreement can be estimated with just unlabeled data. Our prediction algorithm outperforms previous methods both in shifts where agreement-on-the-line holds and, surprisingly, when accuracy is not on the line. This phenomenon also provides new insights into deep neural networks: unlike accuracy-on-the-line, agreement-on-the-line appears to only hold for neural network classifiers.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.13089

2、[CL] Rationale-Augmented Ensembles in Language Models
X Wang, J Wei, D Schuurmans, Q Le, E Chi, D Zhou
[Google Research]
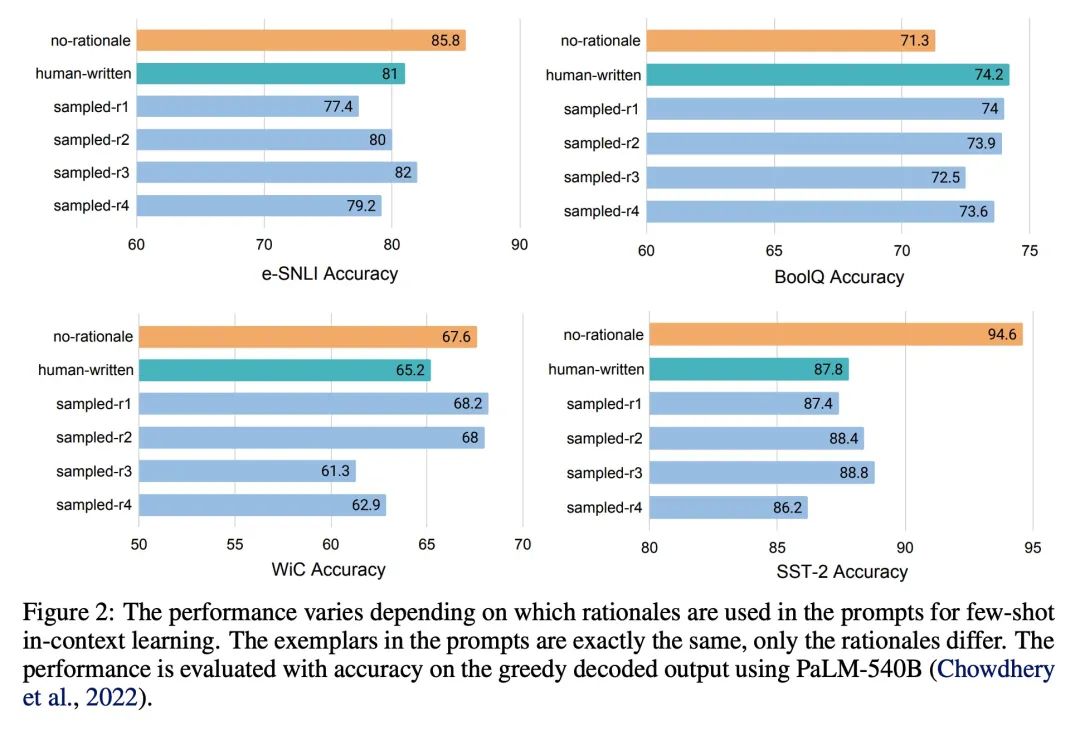
语言模型的理由增强集成。最近的研究表明,理由,或一步步的思维链,可以用来提高多步推理任务的表现。本文重新考虑了理性增强的提示方式,用于少样本上下文学习,其中(输入→输出)提示被扩展为(输入、理由→输出)提示。对于理由增强的提示,证明了现有的依赖于人工提示工程的方法是如何受制于可能损害性能的次优理由的。为了减轻这种脆性,本文提出一种统一的理由增强集成框架,将输出空间中的理由抽样确定为鲁棒地提高性能的关键部分。该框架是通用的,可以很容易地扩展到常见的自然语言处理任务,即使是那些传统上不利用中间步骤的任务,如问答、词义消歧和情感分析。与现有的提示方法——包括没有理由的标准提示和基于理由的思维链提示——相比,理由增强的集成能取得更准确和可解释的结果,同时通过相关的理由提高模型预测的可解释性。
Recent research has shown that rationales, or step-by-step chains of thought, can be used to improve performance in multi-step reasoning tasks. We reconsider rationale-augmented prompting for few-shot in-context learning, where (input → output) Prompts are expanded to (input, rationale → output) prompts. For rationale-augmented prompting we demonstrate how existing approaches, which rely on manual prompt engineering, are subject to sub-optimal rationales that may harm performance. To mitigate this brittleness, we propose a unified framework of rationale-augmented ensembles, where we identify rationale sampling in the output space as the key component to robustly improve performance. This framework is general and can easily be extended to common natural language processing tasks, even those that do not traditionally leverage intermediate steps, such as question answering, word sense disambiguation, and sentiment analysis. We demonstrate that rationale-augmented ensembles achieve more accurate and interpretable results than existing prompting approaches—including standard prompting without rationales and rationale-based chain-of-thought prompting—while simultaneously improving interpretability of model predictions through the associated rationales.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2207.00747


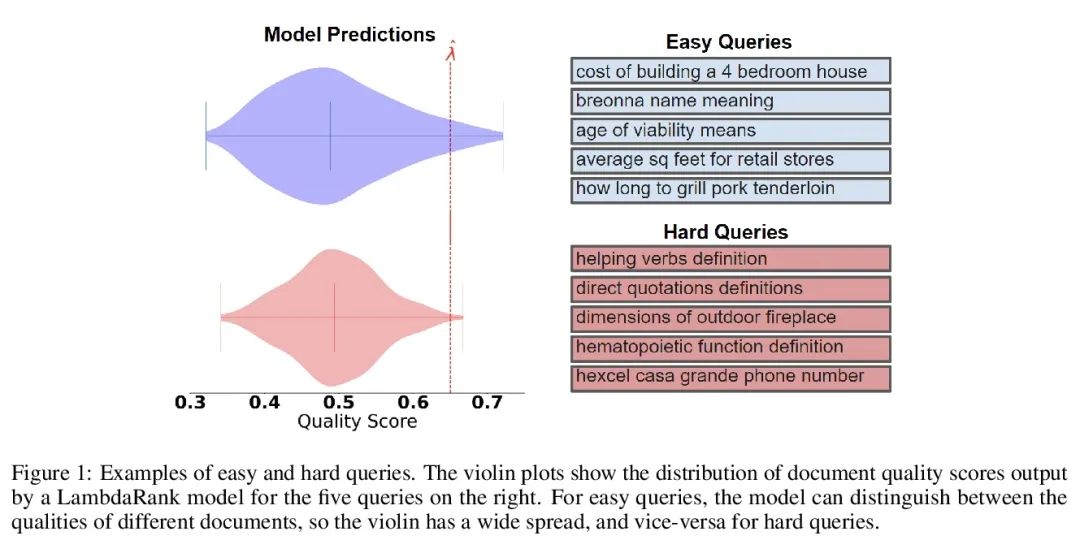
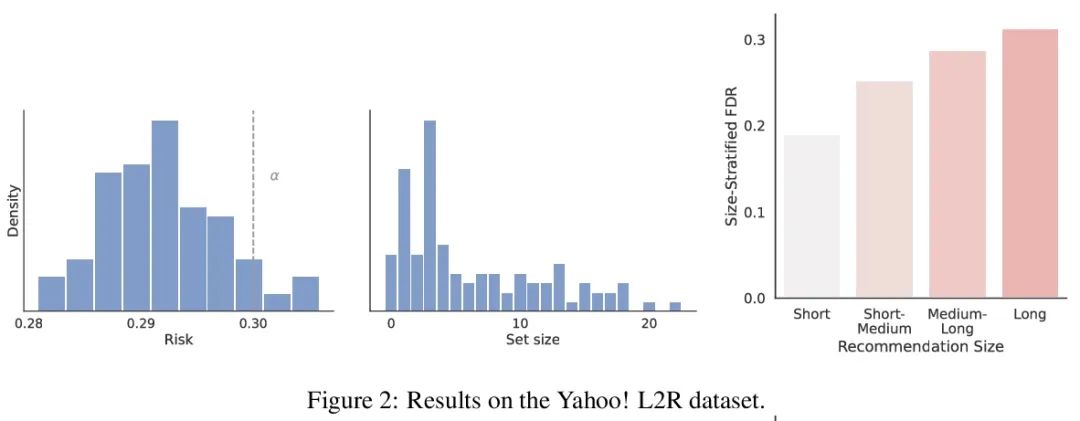
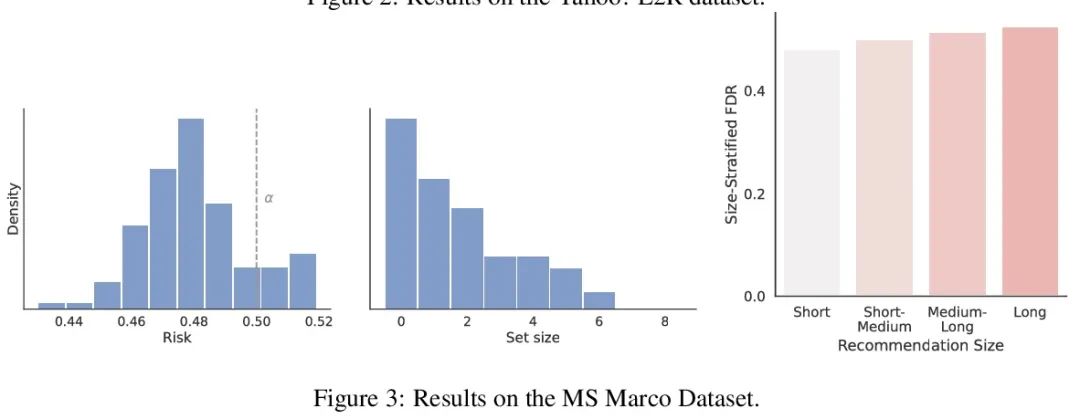
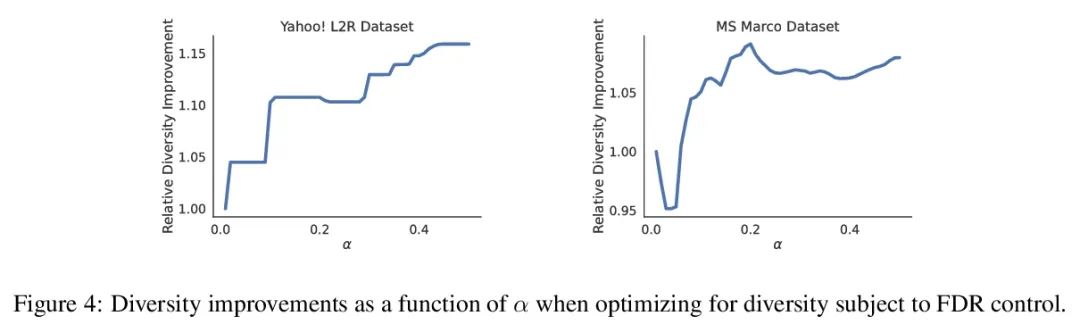
3、[IR] Recommendation Systems with Distribution-Free Reliability Guarantees
A N. Angelopoulos, K Krauth, S Bates, Y Wang, M I. Jordan
[UC Berkeley]
具有无分布可靠性保证的推荐系统。建立推荐系统时,总是试图向用户输出一组有帮助的项目。在系统背后,一个排名模型预测两个候选项目哪个更好,必须将这些成对的比较提炼成面向用户的输出。然而,一个学习得到的排名模型从来都不是完美的,因此,其预测从表面上看不能保证面向用户的输出是可靠的。从一个预训练的排名模型出发,本文展示了如何返回一个严格保证包含大部分好项目的项目集合。该程序赋予任何排名模型以严格错误发现率(FDR)的有限样本控制,无论(未知)数据分布如何。此外,所提出的校准算法使推荐系统中多个目标的整合变得简单而有原则。作为例子,本文展示了如何在用户指定的FDR控制水平下优化推荐多样性,避免了指定多样性损失与精度损失的特殊权重。在整个过程中,专注于学习对一组可能的推荐进行排名的问题,在Yahoo! Learning to Rank和MSMarco数据集上评估了所提出的方法。
When building recommendation systems, we seek to output a helpful set of items to the user. Under the hood, a ranking model predicts which of two candidate items is better, and we must distill these pairwise comparisons into the user-facing output. However, a learned ranking model is never perfect, so taking its predictions at face value gives no guarantee that the user-facing output is reliable. Building from a pre-trained ranking model, we show how to return a set of items that is rigorously guaranteed to contain mostly good items. Our procedure endows any ranking model with rigorous finite-sample control of the false discovery rate (FDR), regardless of the (unknown) data distribution. Moreover, our calibration algorithm enables the easy and principled integration of multiple objectives in recommender systems. As an example, we show how to optimize for recommendation diversity subject to a user-specified level of FDR control, circumventing the need to specify ad hoc weights of a diversity loss against an accuracy loss. Throughout, we focus on the problem of learning to rank a set of possible recommendations, evaluating our methods on the Yahoo! Learning to Rank and MSMarco datasets.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2207.01609

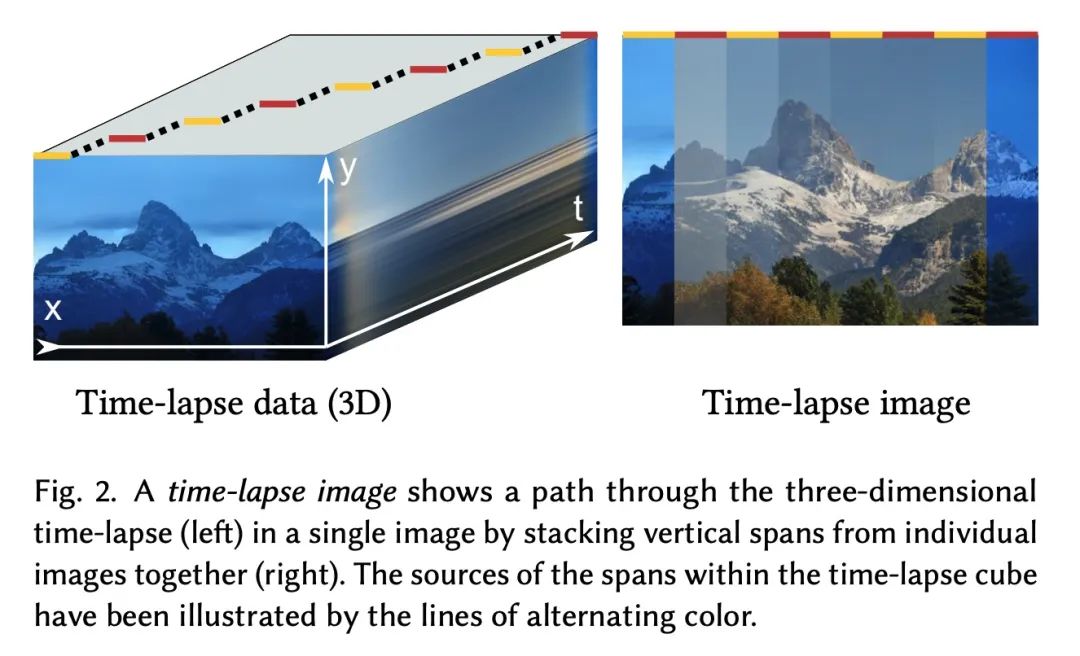
4、[CV] Disentangling Random and Cyclic Effects in Time-Lapse Sequences
E Härkönen, M Aittala, T Kynkäänniemi, S Laine, T Aila, J Lehtinen
[Aalto University & NVIDIA]
延时摄影序列随机与循环效应的解缠。延时摄影序列提供了视觉上令人信服的对动态过程的洞察,这些过程太慢,无法实时观察。然而,由于随机效应(如天气)和周期效应(如昼夜循环)的影响,以视频形式回放一个长的延时摄影序列往往会导致干扰性的闪烁。本文提出延时序列解缠问题,允许对图像中的整体趋势、周期性效应和随机效应进行单独的事后控制,并描述了一种基于数据驱动的生成模型的技术来实现这一目标。能以单独输入图像不可能实现的方式”重渲染”序列。例如,可以稳定一个长序列,在可选择的、一致的天气下,关注植物在多个月内的生长。所提出方法是基于生成对抗网络(GAN),以延时摄影序列的时间坐标为条件。其结构和训练程序是这样设计的:网络学会使用GAN的潜空间来模拟随机变化,如天气,并通过用具有特定频率的傅里叶特征向模型提供条件时间标签,来区分总体趋势和周期性变化。实验表明,所提出模型对训练数据中的缺陷具有鲁棒性,能修正捕捉长延时序列的一些实际困难,如临时遮挡、不均匀的帧间隔和帧缺失。
Time-lapse image sequences offer visually compelling insights into dynamic processes that are too slow to observe in real time. However, playing a long time-lapse sequence back as a video often results in distracting flicker due to random effects, such as weather, as well as cyclic effects, such as the day-night cycle. We introduce the problem of disentangling time-lapse sequences in a way that allows separate, after-the-fact control of overall trends, cyclic effects, and random effects in the images, and describe a technique based on data-driven generative models that achieves this goal. This enables us to “re-render” the sequences in ways that would not be possible with the input images alone. For example, we can stabilize a long sequence to focus on plant growth over many months, under selectable, consistent weather. Our approach is based on Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN) that are conditioned with the time coordinate of the time-lapse sequence. Our architecture and training procedure are designed so that the networks learn to model random variations, such as weather, using the GAN’s latent space, and to disentangle overall trends and cyclic variations by feeding the conditioning time label to the model using Fourier features with specific frequencies. We show that our models are robust to defects in the training data, enabling us to amend some of the practical difficulties in capturing long time-lapse sequences, such as temporary occlusions, uneven frame spacing, and missing frames.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2207.01413



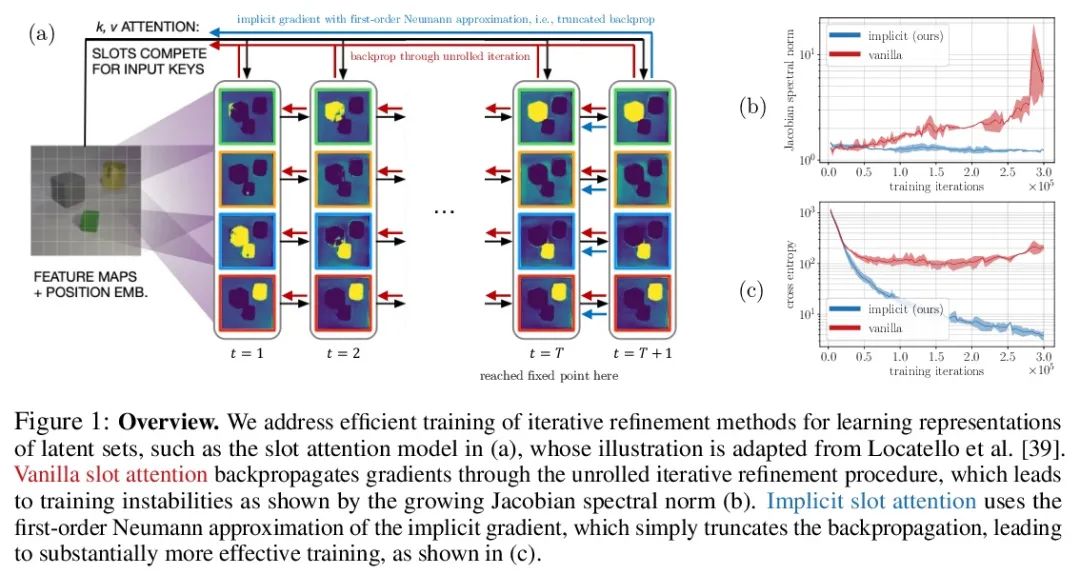
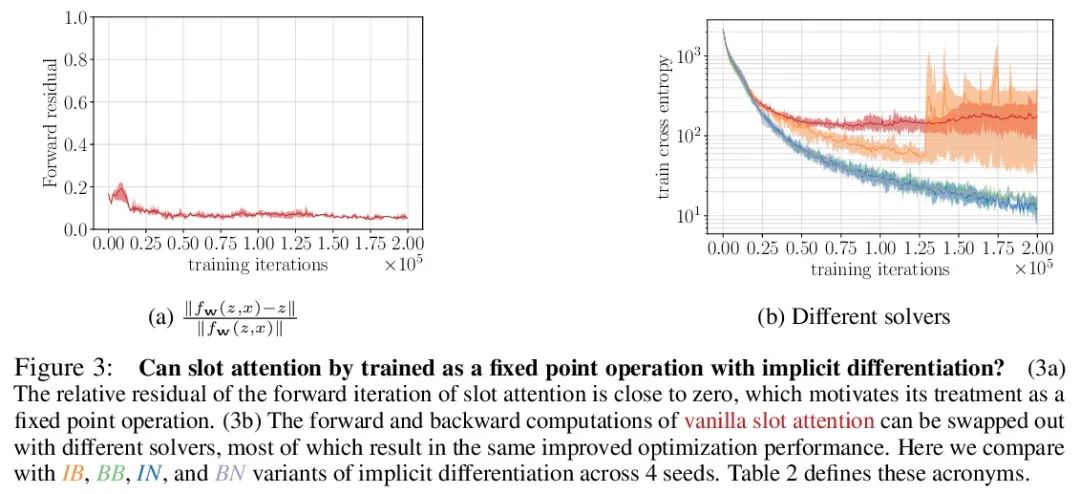
5、[LG] Object Representations as Fixed Points: Training Iterative Refinement Algorithms with Implicit Differentiation
M Chang, T L. Griffiths, S Levine
[UC Berkeley & Princeton University]
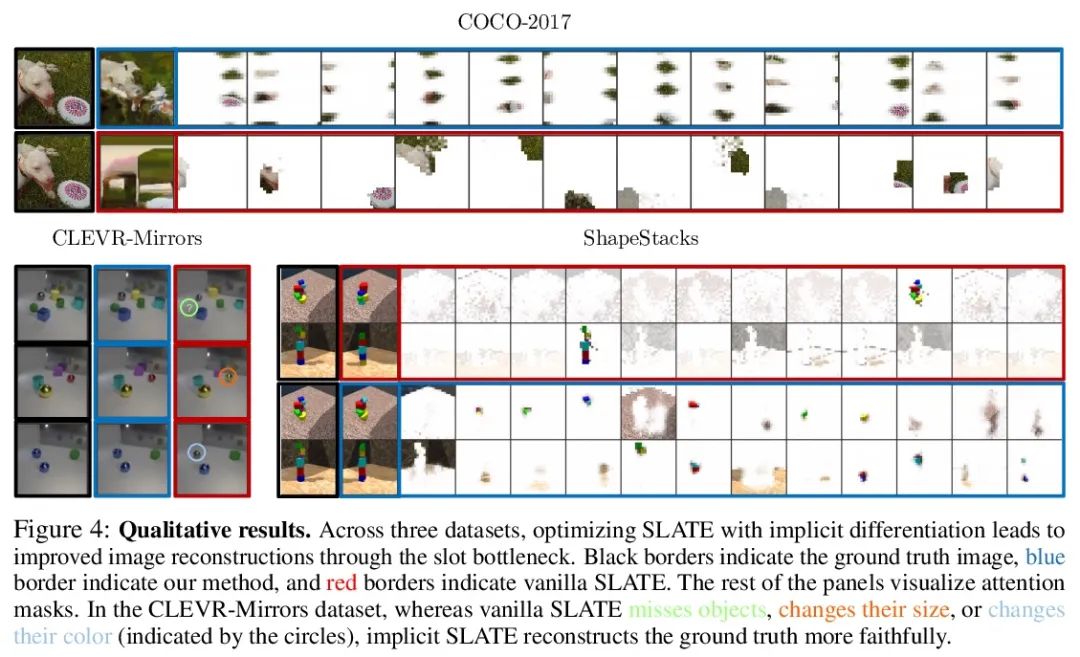
定点对象表示:基于隐式差分的迭代细化算法训练。迭代改进——从随机猜测开始,然后迭代改进猜测——是一种有用的表示学习范式,提供了一种方法来打破对数据同样合理的解释间的对称性。这一特性使得该方法能应用于推断实体集合的表示,如物理场景中的物体,在结构上类似于潜空间中的聚类算法。然而,大多数之前的工作是通过松散细化过程来微分,这可能会使优化具有挑战性。本文观察到通过隐函数定理该方法可变得可微,并开发了一种隐式微分的方法,通过解耦前向和后向,提高训练的稳定性和可操作性。这种联系使得能应用优化隐含层的进展,不仅改善了SLATE中槽注意力模块的优化——一种最先进的实体表示学习方法——而且在反向传播的空间和时间复杂度不变的情况下,只需增加一行代码就能做到。
Iterative refinement – start with a random guess, then iteratively improve the guess – is a useful paradigm for representation learning because it offers a way to break symmetries among equally plausible explanations for the data. This property enables the application of such methods to infer representations of sets of entities, such as objects in physical scenes, structurally resembling clustering algorithms in latent space. However, most prior works differentiate through the unrolled refinement process, which can make optimization challenging. We observe that such methods can be made differentiable by means of the implicit function theorem, and develop an implicit differentiation approach that improves the stability and tractability of training by decoupling the forward and backward passes. This connection enables us to apply advances in optimizing implicit layers to not only improve the optimization of the slot attention module in SLATE, a state-of-the-art method for learning entity representations, but do so with constant space and time complexity in backpropagation and only one additional line of code.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2207.00787



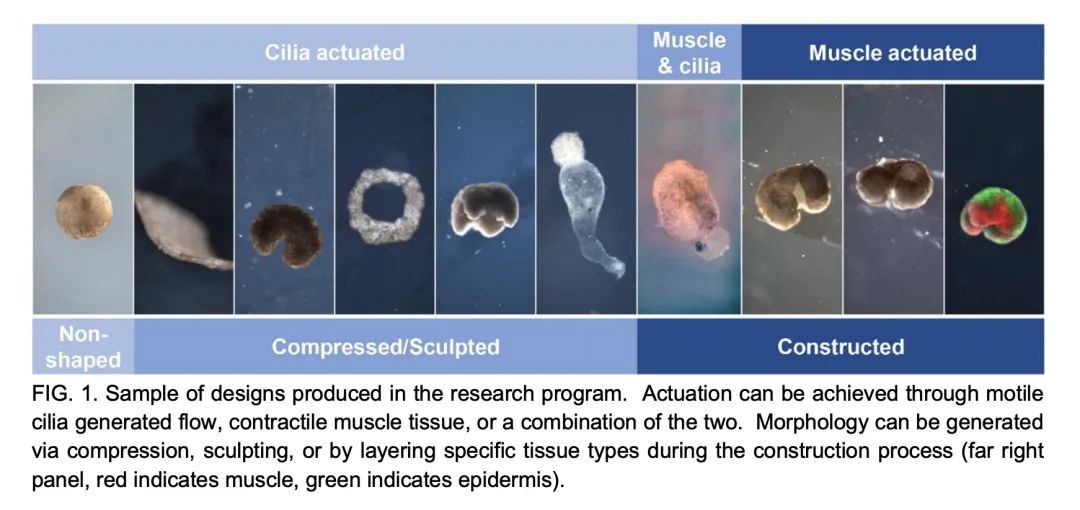
[RO] Biological Robots: Perspectives on an Emerging Interdisciplinary Field
生物机器人:新兴跨学科领域综述
D. Blackiston, S. Kriegman, J. Bongard, M. Levin
[Tufts University & University of Vermont]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2207.00880


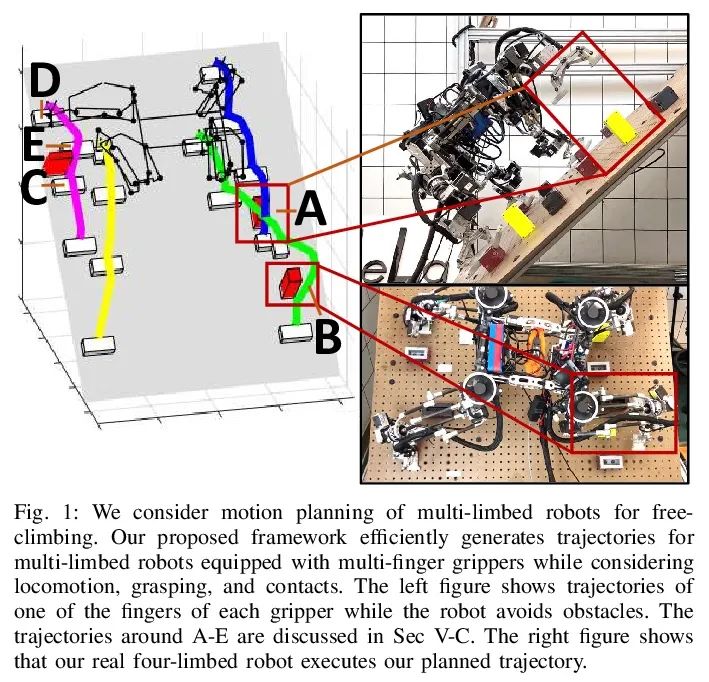
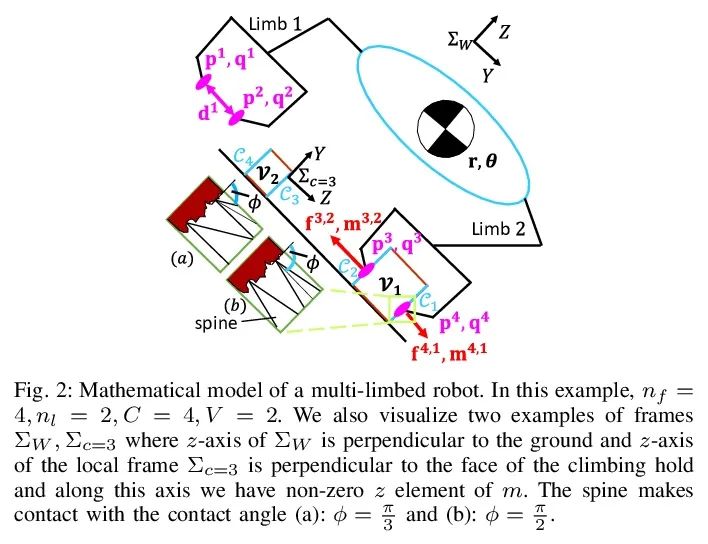
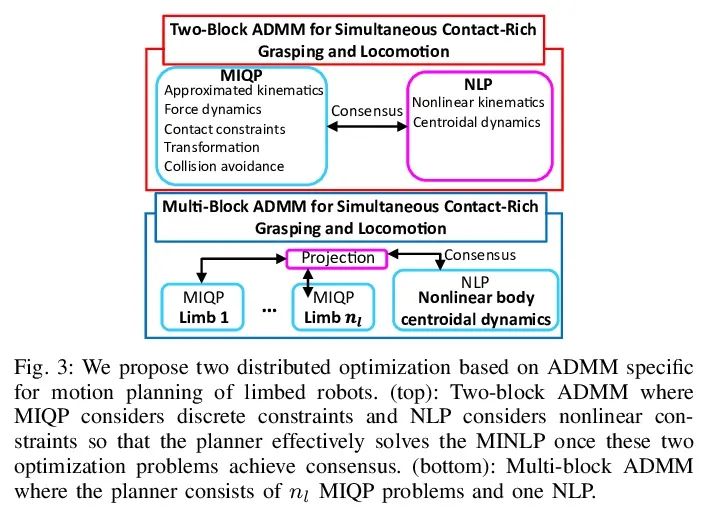
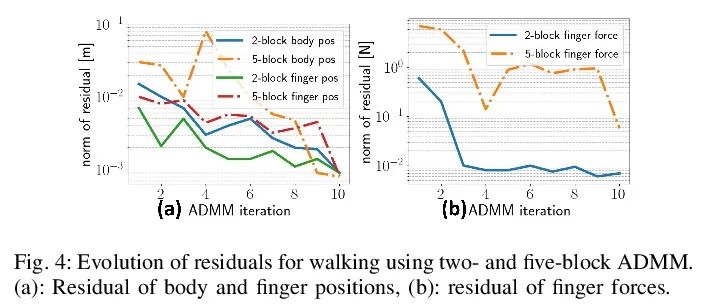
[RO] Simultaneous Contact-Rich Grasping and Locomotion via Distributed Optimization Enabling Free-Climbing for Multi-Limbed Robots
通过分布式优化实现多肢机器人自由攀爬同时接触丰富抓取与运动
Y Shirai, X Lin, A Schperberg, Y Tanaka…
[University of California, Los Angeles]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2207.01418

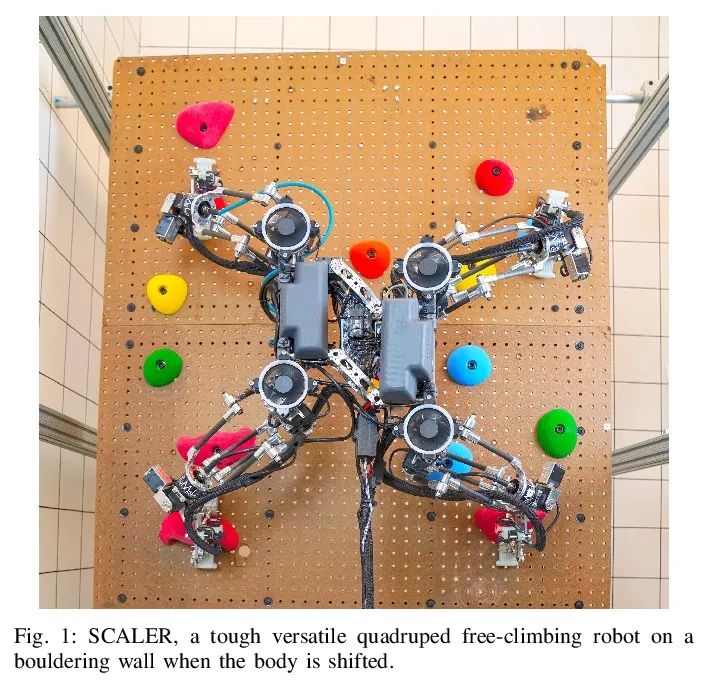
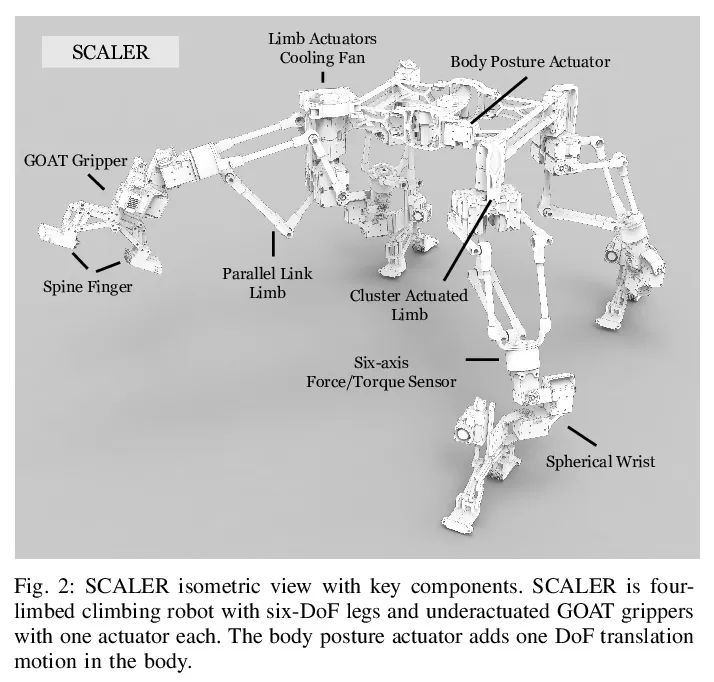
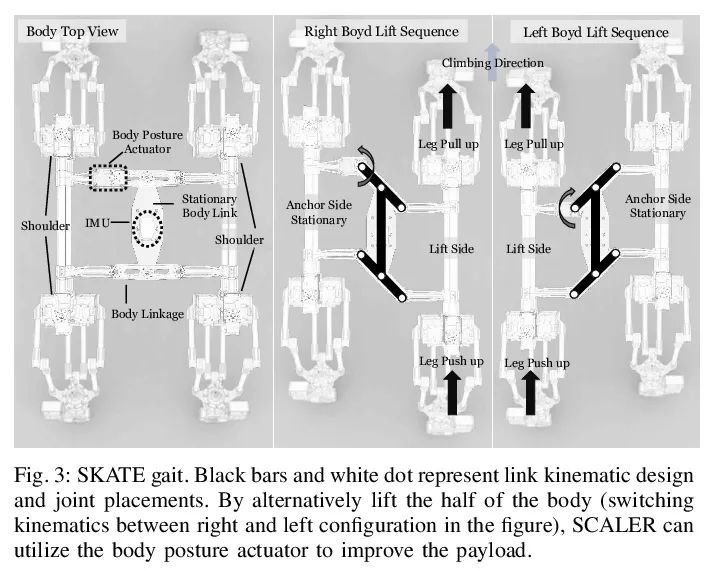
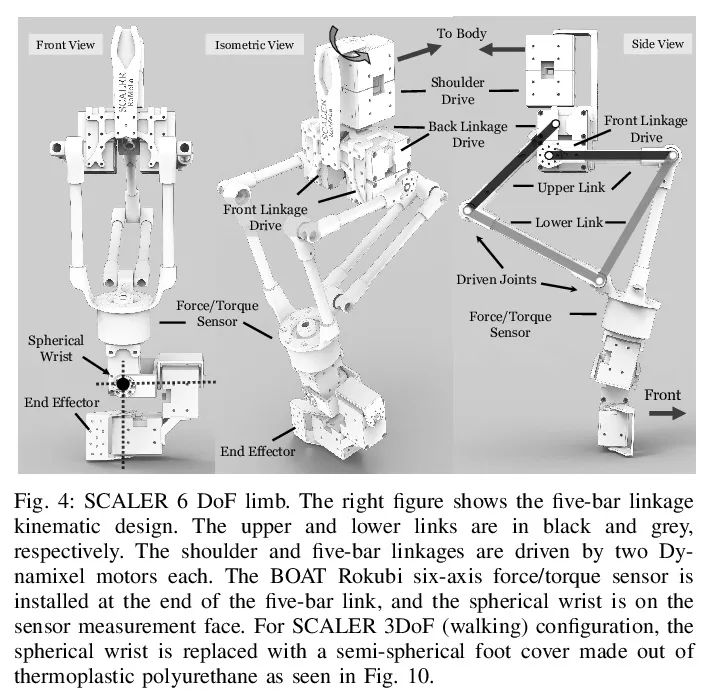
[RO] SCALER: A Tough Versatile Quadruped Free-Climber Robot
SCALER:坚固多功能四足自由攀爬机器人
Y Tanaka, Y Shirai, X Lin, A Schperberg, H Kato, A Swerdlow, N Kumagai, D Hong
[University of California, Los Angeles]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2207.01180

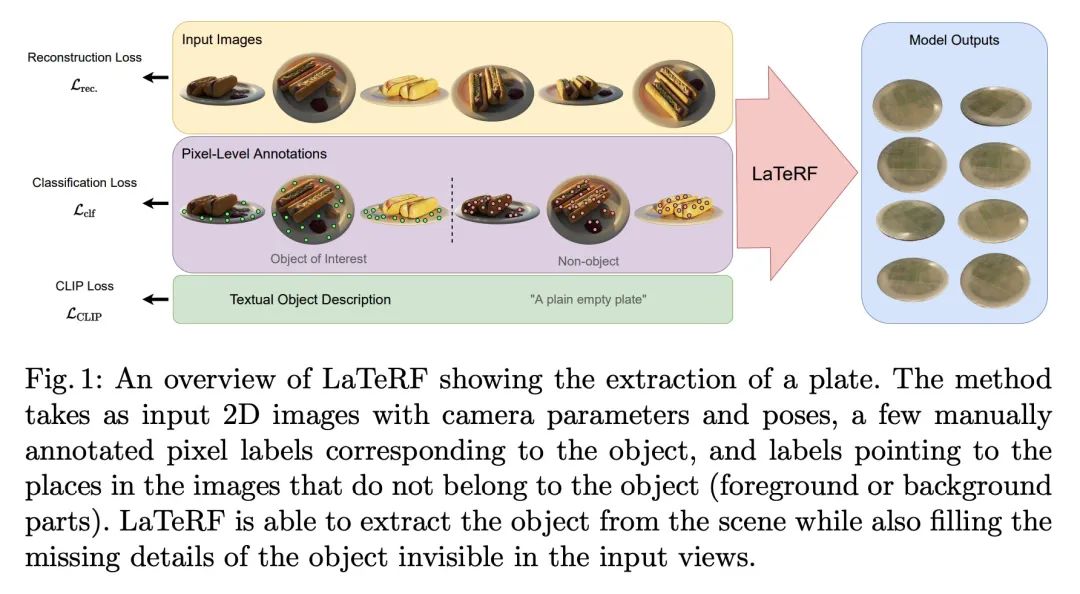
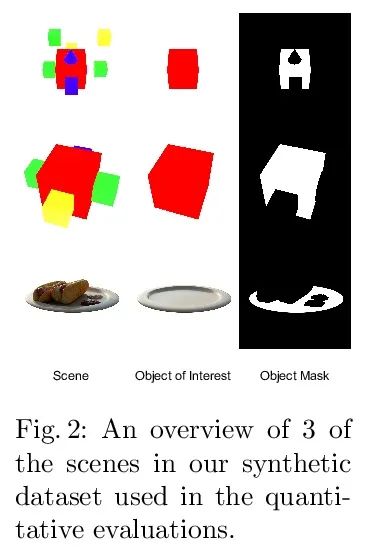
[CV] LaTeRF: Label and Text Driven Object Radiance Fields
LaTeRF:标签和文本驱动的对象辐射场
A Mirzaei, Y Kant, J Kelly, I Gilitschenski
[University of Toronto]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2207.01583