LG – 机器学习 CV – 计算机视觉 CL – 计算与语言 AS – 音频与语音 RO – 机器人
转自爱可可爱生活
摘要:用数据修剪战胜神经网络幂律扩展率、生成式神经人体辐射场、逆向问题中深度学习方法的理论分析、贝叶斯因果推断的批判性综述、可复现高效协作型优化基准、基于可微姿态估计的3D多目标跟踪、提炼模型失效模式作为潜空间方向、面向开放式文本生成的事实性增强语言模型、面向动态视图合成快速优化的神经可变形体素网格
1、[LG] Beyond neural scaling laws: beating power law scaling via data pruning
B Sorscher, R Geirhos, S Shekhar, S Ganguli, A S. Morcos
[Stanford University & University of Tübingen & Meta AI]
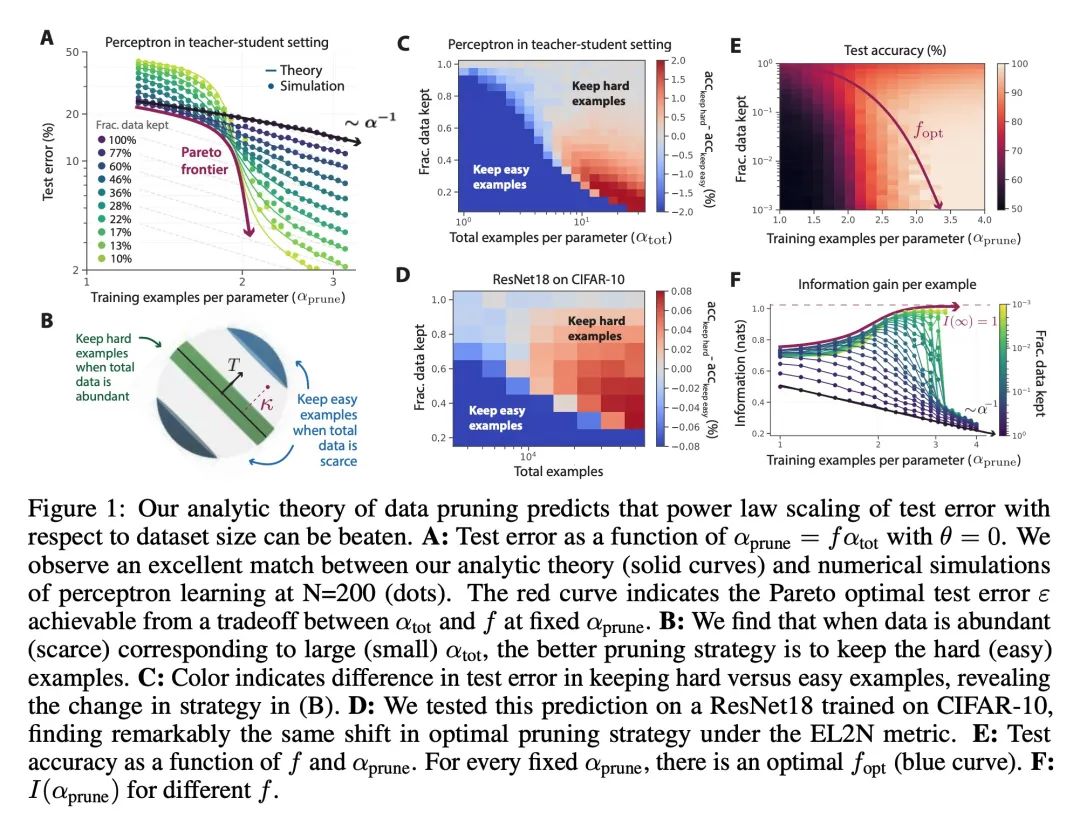
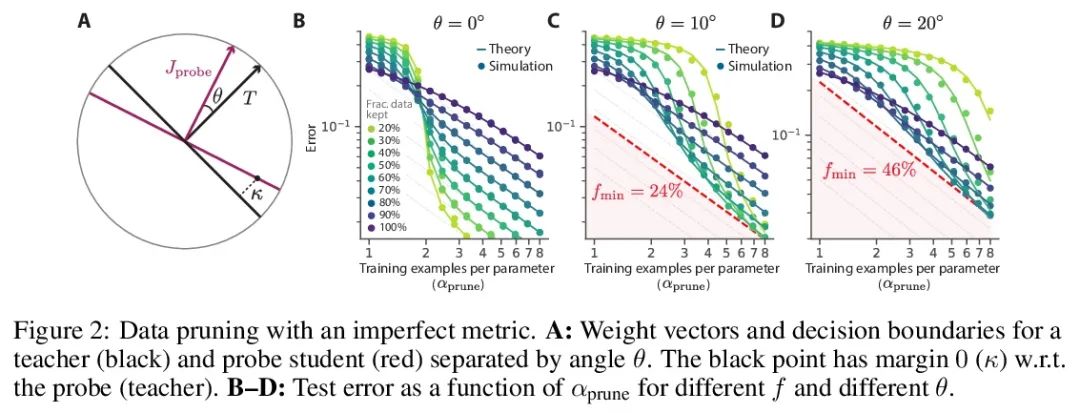
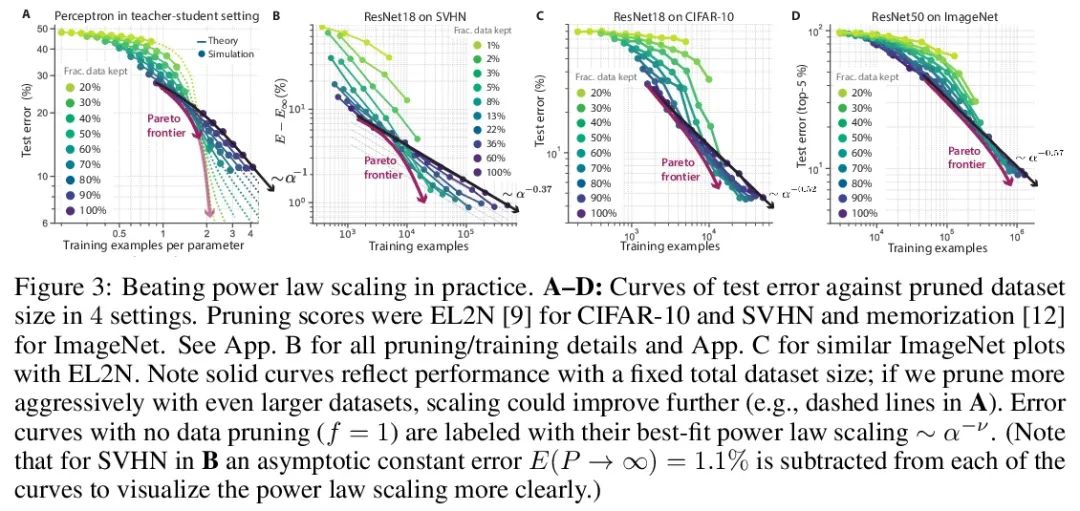
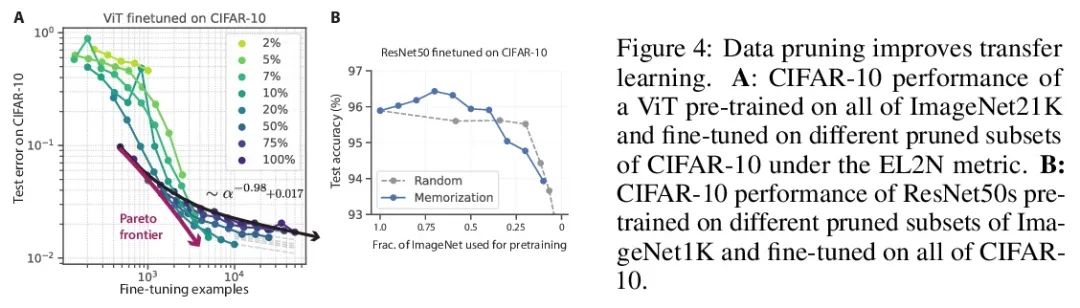
超越神经缩放律:用数据修剪战胜幂律缩放。广泛观察到的神经缩放律,即误差随着训练集大小、模型大小或两者幂指数下降,推动了深度学习性能大幅提升。然而,仅通过扩展来实现这些改进需要相当大的计算和能源成本。本文专注于误差与数据集大小的比例关系,并展示了在理论和实践中,如果有高质量的数据修剪指标,以将训练样本按应丢弃的顺序排列,实现任何修剪后的数据集大小,就可以突破幂律比例,将其减小到指数比例。本文根据经验测试了这个新的指数缩放预测与剪枝数据集的大小,确实观察到在CIFAR10、SVHN和ImageNet上训练的ResNets的缩放性能优于幂律缩放。鉴于寻找高质量修剪指标的重要性,在ImageNet上对10个不同的数据剪枝指标进行了首次大规模的基准研究。发现大多数现有的高性能指标在ImageNet上的扩展性很差,而最好的指标是计算密集型的,并且需要为每张图片打标签。因此,本文开发了一个新的简单、便宜、可扩展的自监督修剪指标,其性能与最佳监督指标相当。本文工作表明,发现好的数据修剪指标可能会提供一条可行的路径,以大幅改善神经缩放律,降低现代深度学习的资源成本。
Widely observed neural scaling laws, in which error falls off as a power of the training set size, model size, or both, have driven substantial performance improvements in deep learning. However, these improvements through scaling alone require considerable costs in compute and energy. Here we focus on the scaling of error with dataset size and show how both in theory and practice we can break beyond power law scaling and reduce it to exponential scaling instead if we have access to a high-quality data pruning metric that ranks the order in which training examples should be discarded to achieve any pruned dataset size. We then test this new exponential scaling prediction with pruned dataset size empirically, and indeed observe better than power law scaling performance on ResNets trained on CIFAR10, SVHN, and ImageNet. Given the importance of finding high-quality pruning metrics, we perform the first large-scale benchmarking study of ten different data pruning metrics on ImageNet. We find most existing high performing metrics scale poorly to ImageNet, while the best are computationally intensive and require labels for every image. We therefore developed a new simple, cheap and scalable self-supervised pruning metric that demonstrates comparable performance to the best supervised metrics. Overall, our work suggests that the discovery of good data-pruning metrics may provide a viable path forward to substantially improved neural scaling laws, thereby reducing the resource costs of modern deep learning.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.14486

2、[CV] Generative Neural Articulated Radiance Fields
A W. Bergman, P Kellnhofer, Y Wang, E R. Chan, D B. Lindell, G Wetzstein
[Stanford University & TU Delft]
生成式神经人体辐射场。最近,仅用单视角2D照片集的3D感知生成对抗网络(GAN)的无监督学习取得了很大进展。然而,这些3D生成对抗网络还没有被证明适用于人体,而且现有框架生成的辐射场不能直接编辑,限制了它们在下游任务中的适用性。本文提出一种解决这些挑战的方案,开发了一种3D GAN框架,可以学习生成典型姿态下的人体或人脸的辐射场,用显式的变形场将其扭曲成所需的身体姿态或面部表情。使用该框架,展示了第一个高质量的人体辐射场生成结果。与没有经过显式变形训练的3D GAN相比,本文提出的变形感知训练程序在编辑人体姿态或人脸表情时明显提高了生成的人体或人脸的质量。
Widely observed neural scaling laws, in which error falls off as a power of the training set size, model size, or both, have driven substantial performance improvements in deep learning. However, these improvements through scaling alone require considerable costs in compute and energy. Here we focus on the scaling of error with dataset size and show how both in theory and practice we can break beyond power law scaling and reduce it to exponential scaling instead if we have access to a high-quality data pruning metric that ranks the order in which training examples should be discarded to achieve any pruned dataset size. We then test this new exponential scaling prediction with pruned dataset size empirically, and indeed observe better than power law scaling performance on ResNets trained on CIFAR10, SVHN, and ImageNet. Given the importance of finding high-quality pruning metrics, we perform the first large-scale benchmarking study of ten different data pruning metrics on ImageNet. We find most existing high performing metrics scale poorly to ImageNet, while the best are computationally intensive and require labels for every image. We therefore developed a new simple, cheap and scalable self-supervised pruning metric that demonstrates comparable performance to the best supervised metrics. Overall, our work suggests that the discovery of good data-pruning metrics may provide a viable path forward to substantially improved neural scaling laws, thereby reducing the resource costs of modern deep learning.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.14314


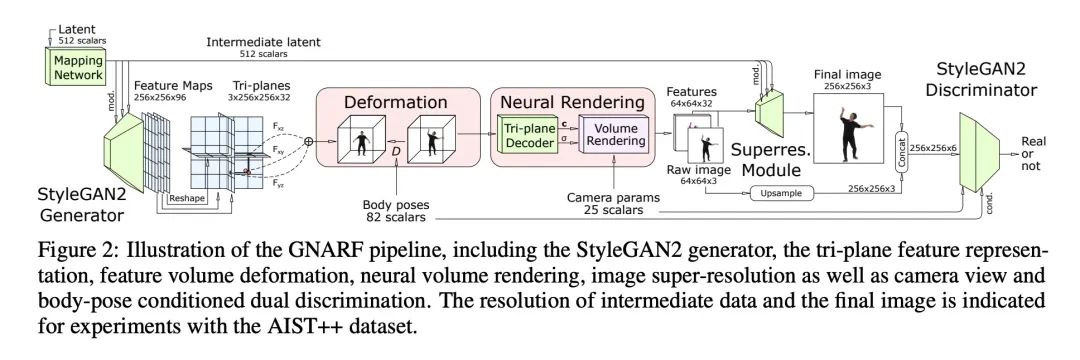


3、[LG] Theoretical Perspectives on Deep Learning Methods in Inverse Problems
J Scarlett, R Heckel, M R. D. Rodrigues, P Hand, Y C. Eldar
[National University of Singapore & Technical University of Munich & University College London & Northeastern University]
逆向问题中深度学习方法的理论分析。近年来,深度学习方法在逆向问题中的应用取得了重大进展,如去噪、压缩感应、绘画和超分辨率。虽然这一系列的工作主要是由实际的算法和实验推动的,但它也产生了各种有趣的理论问题。本文调研了这一系列工作中一些突出的理论发展,特别是关注生成式预设、未经训练的神经网络预设和展开式算法。除了总结这些主题的现有成果外,还强调了几个面临的挑战和开放性问题。尽管这一行的工作发展迅速,但本文认为该主题仍处于早期阶段,许多最令人振奋的发展还在后面。
In recent years, there have been significant advances in the use of deep learning methods in inverse problems such as denoising, compressive sensing, inpainting, and super-resolution. While this line of works has predominantly been driven by practical algorithms and experiments, it has also given rise to a variety of intriguing theoretical problems. In this paper, we survey some of the prominent theoretical developments in this line of works, focusing in particular on generative priors, untrained neural network priors, and unfolding algorithms. In addition to summarizing existing results in these topics, we highlight several ongoing challenges and open problems.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.14373



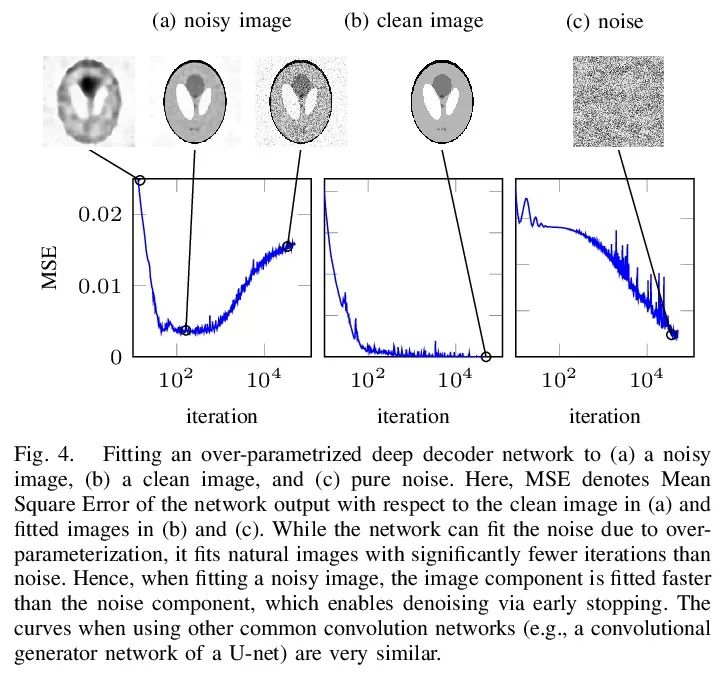
4、[LG] Bayesian Causal Inference: A Critical Review
F Li, P Ding, F Mealli
[Duke University & UC Berkeley & University of Florence]
贝叶斯因果推断:批判性综述。本文对基于潜在结果框架的贝叶斯因果推断观点进行了批判性回顾。回顾了因果估计、识别假设和贝叶斯因果推断的一般结构,强调了贝叶斯因果推断所特有的问题,包括倾向分数的作用、可识别性的定义以及低维和高维场景下的先验选择。本文指出了协变量重叠的核心作用,以及贝叶斯因果推断中更普遍的设计阶段。将讨论扩展到两个复杂的分配机制:工具变量和时间变化的处理。对于因果推断,甚至是统计学中的一切,贝叶斯应该是工具,而不是目标。
This paper provides a critical review of the Bayesian perspective of causal inference based on the potential outcomes framework. We review the causal estimands, identification assumptions, and general structure of Bayesian inference of causal effects. We highlight issues that are unique to Bayesian causal inference, including the role of the propensity score, definition of identifiability, and choice of priors in both low and high dimensional regimes. We point out the central role of covariate overlap and more generally the design stage in Bayesian causal inference. We extend the discussion to two complex assignment mechanisms: instrumental variable and time-varying treatments. Throughout, we illustrate the key concepts via examples.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.15460

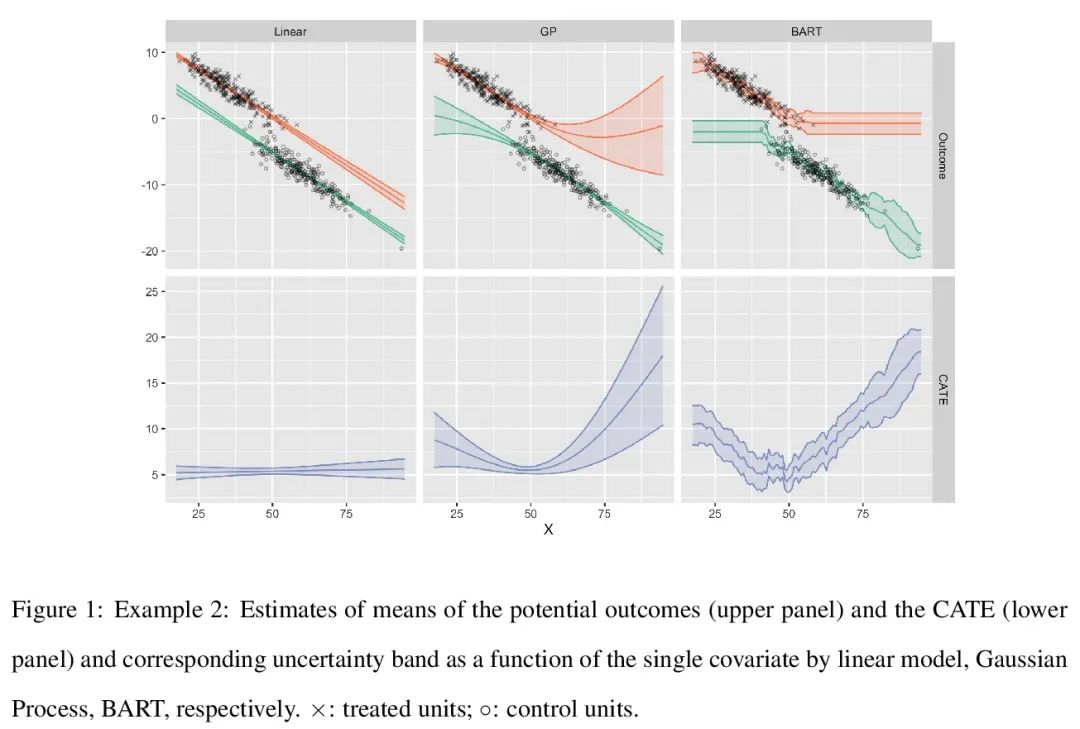
5、[LG] Benchopt: Reproducible, efficient and collaborative optimization benchmarks
T Moreau, M Massias, A Gramfort, P Ablin, P Bannier, B Charlier…
[Université Paris-Saclay & Univ Lyon & Université Paris-Dauphine…]
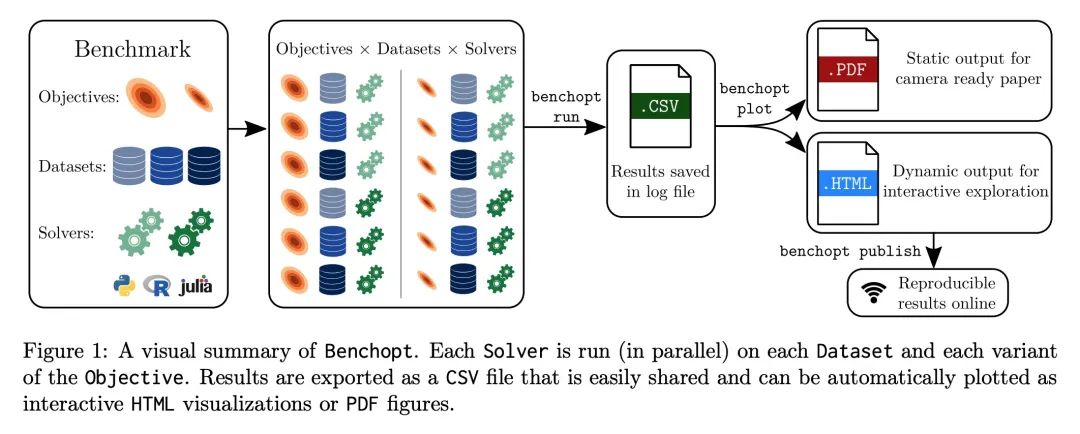
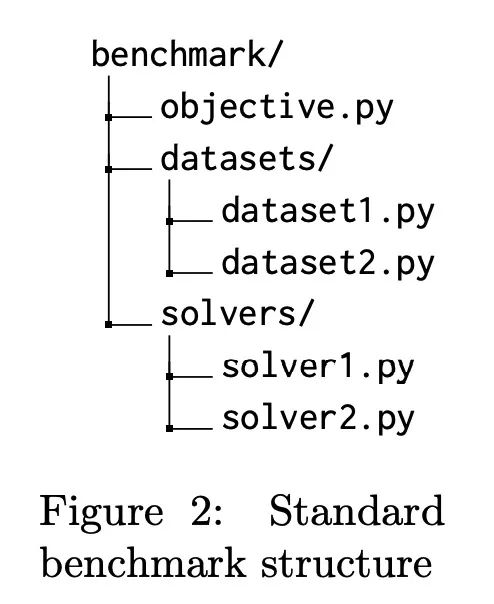
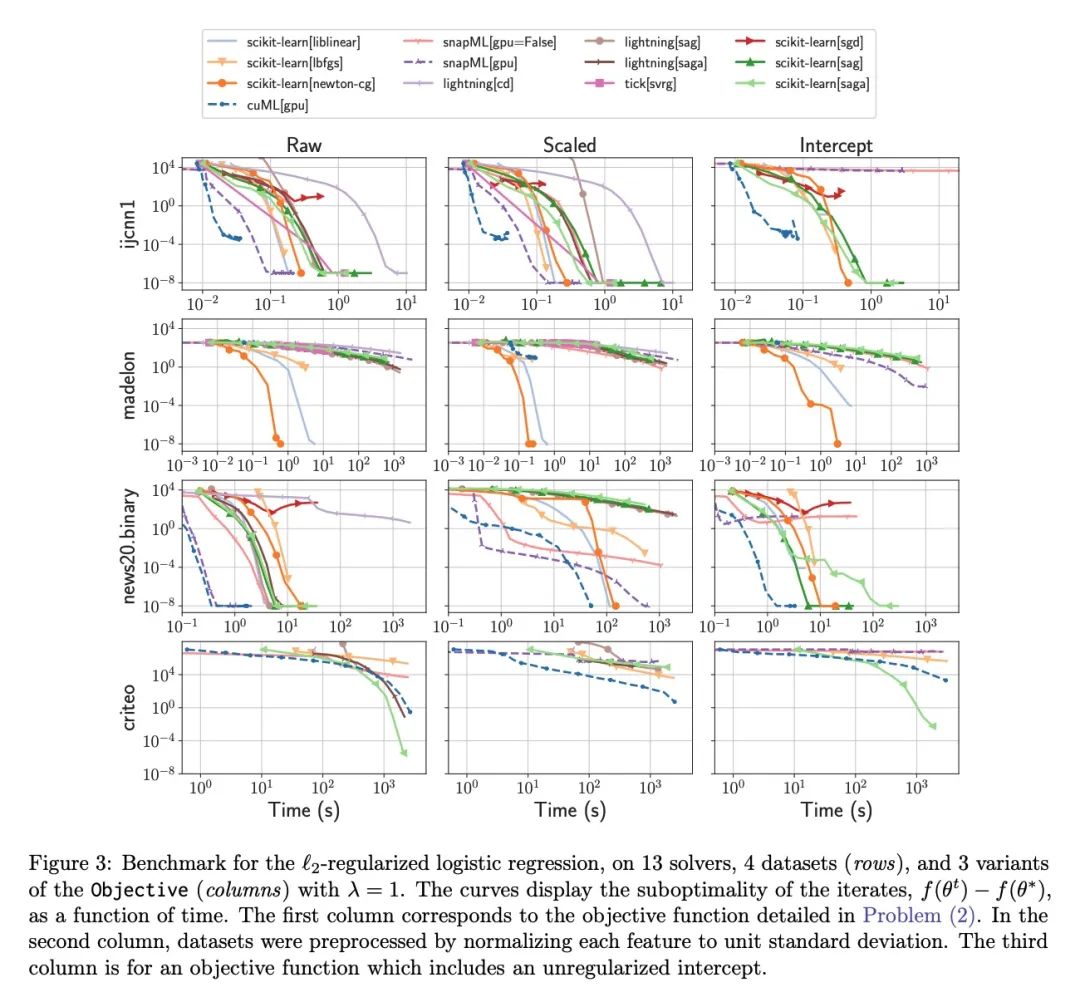
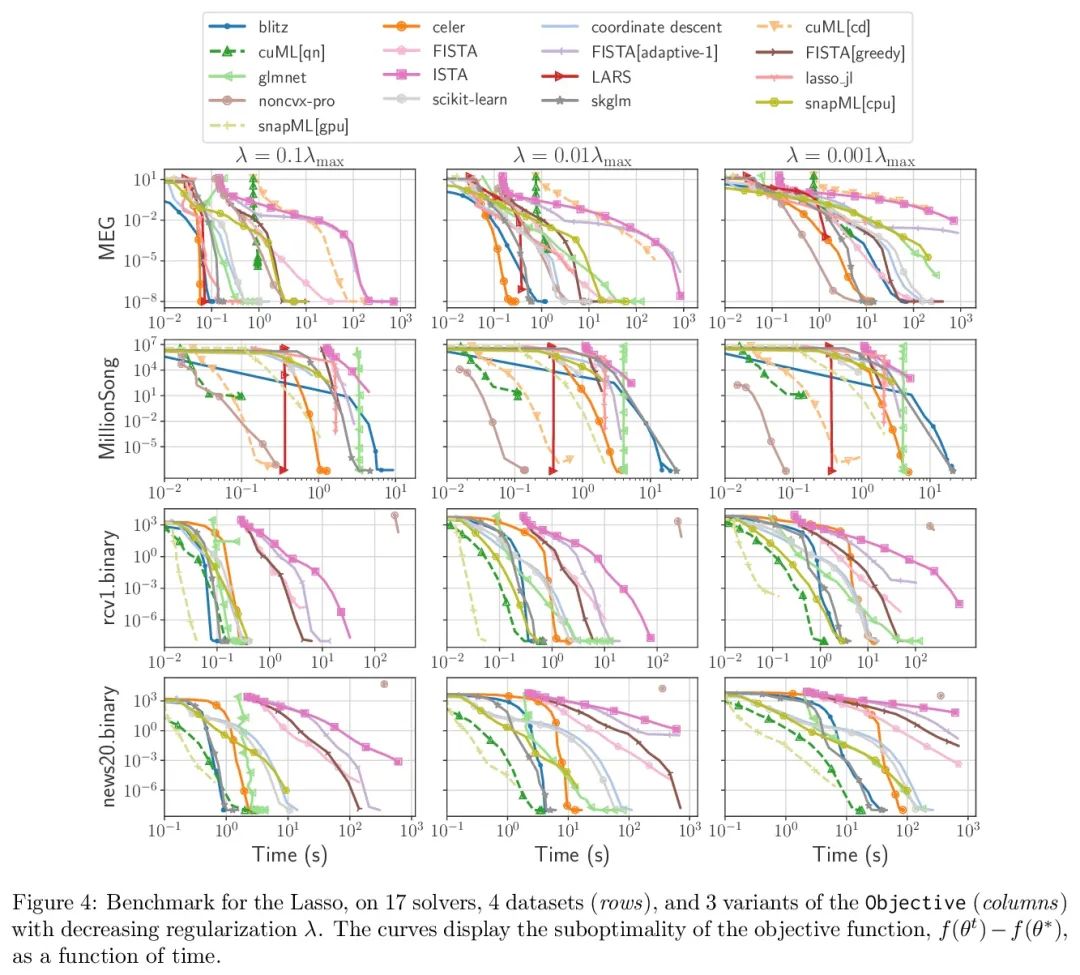
Benchopt: 可复现高效协作型优化基准。数值验证是机器学习研究的核心,因为它可以评估新方法的实际影响,并确认理论和实践之间的一致性。然而,该领域的快速发展带来了一些挑战:研究人员面临着大量需要比较的方法,有限的透明度和对最佳实践的共识,以及繁琐的复现工作。因此,验证往往是非常片面的,这可能导致错误的结论,减缓研究的进展。本文提出Benchopt,一种写作框架,用于自动化、复现和发布跨编程语言和硬件架构的机器学习的优化基准。Benchopt通过提供一个现成的工具来运行、共享和扩展实验,简化了社区的基准测试。为了证明其广泛的实用性,本文展示了三个标准学习任务的基准:L2-正则logistic回归,Lasso,以及用于图像分类的ResNet18训练。这些基准突出了关键的实际发现,对这些问题的最先进水平给出了更细致的看法,表明对于实际评估来说,魔鬼就在细节中。希望Benchopt能够促进社区的合作,从而提高研究结果的可复现性。
Numerical validation is at the core of machine learning research as it allows to assess the actual impact of new methods, and to confirm the agreement between theory and practice. Yet, the rapid development of the field poses several challenges: researchers are confronted with a profusion of methods to compare, limited transparency and consensus on best practices, as well as tedious re-implementation work. As a result, validation is often very partial, which can lead to wrong conclusions that slow down the progress of research. We propose Benchopt, a collaborative framework to automate, reproduce and publish optimization benchmarks in machine learning across programming languages and hardware architectures. Benchopt simplifies benchmarking for the community by providing an off-the-shelf tool for running, sharing and extending experiments. To demonstrate its broad usability, we showcase benchmarks on three standard learning tasks: `2-regularized logistic regression, Lasso, and ResNet18 training for image classification. These benchmarks highlight key practical findings that give a more nuanced view of the state-of-the-art for these problems, showing that for practical evaluation, the devil is in the details. We hope that Benchopt will foster collaborative work in the community hence improving the reproducibility of research findings.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.13424

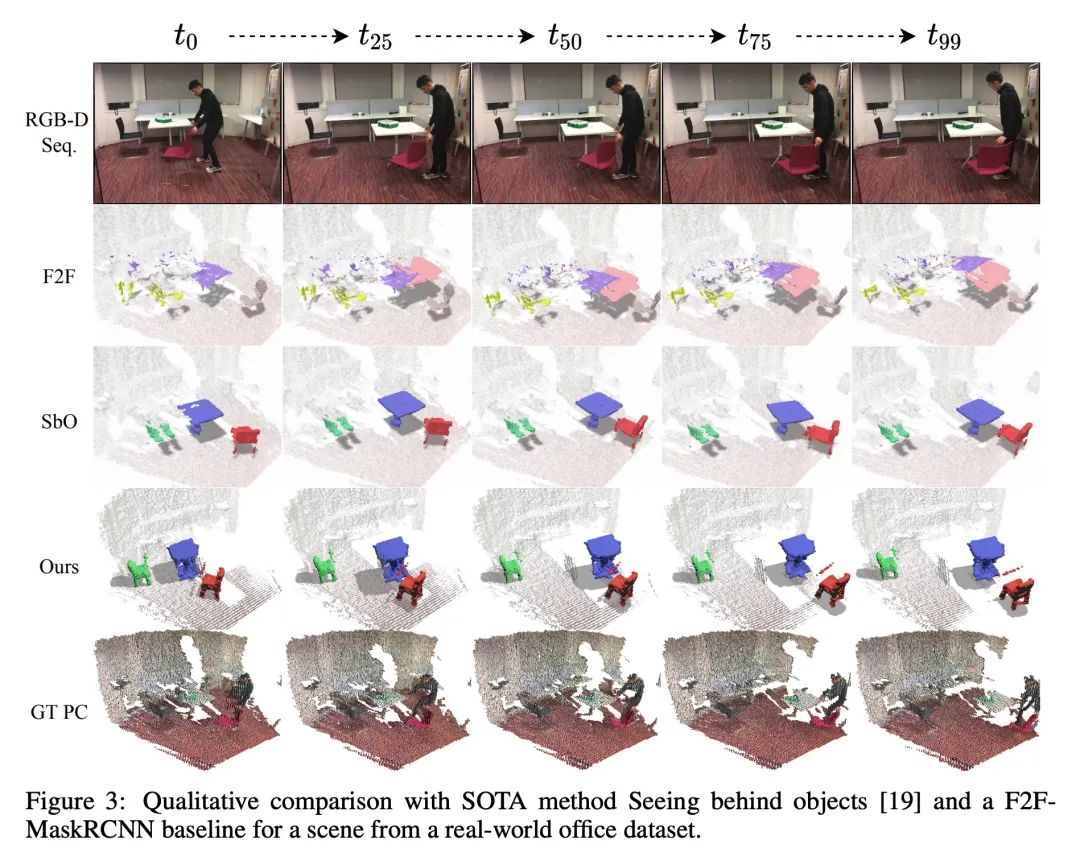
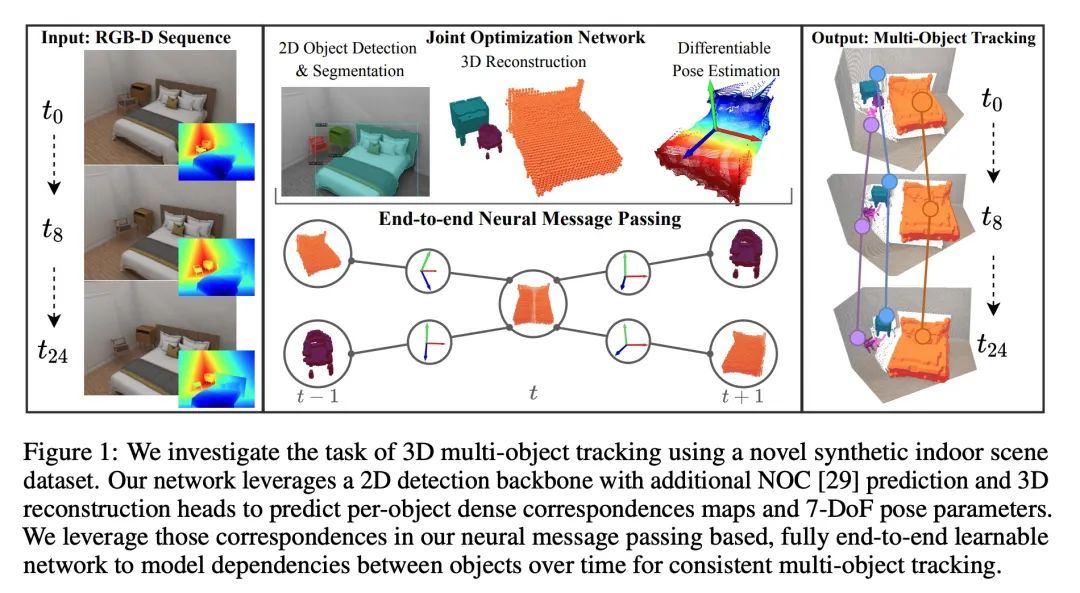
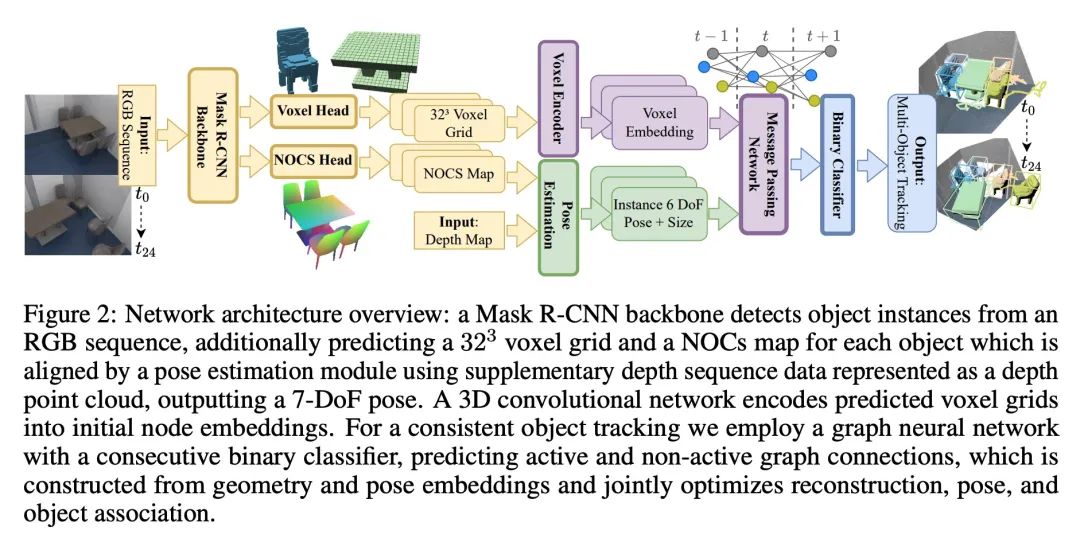
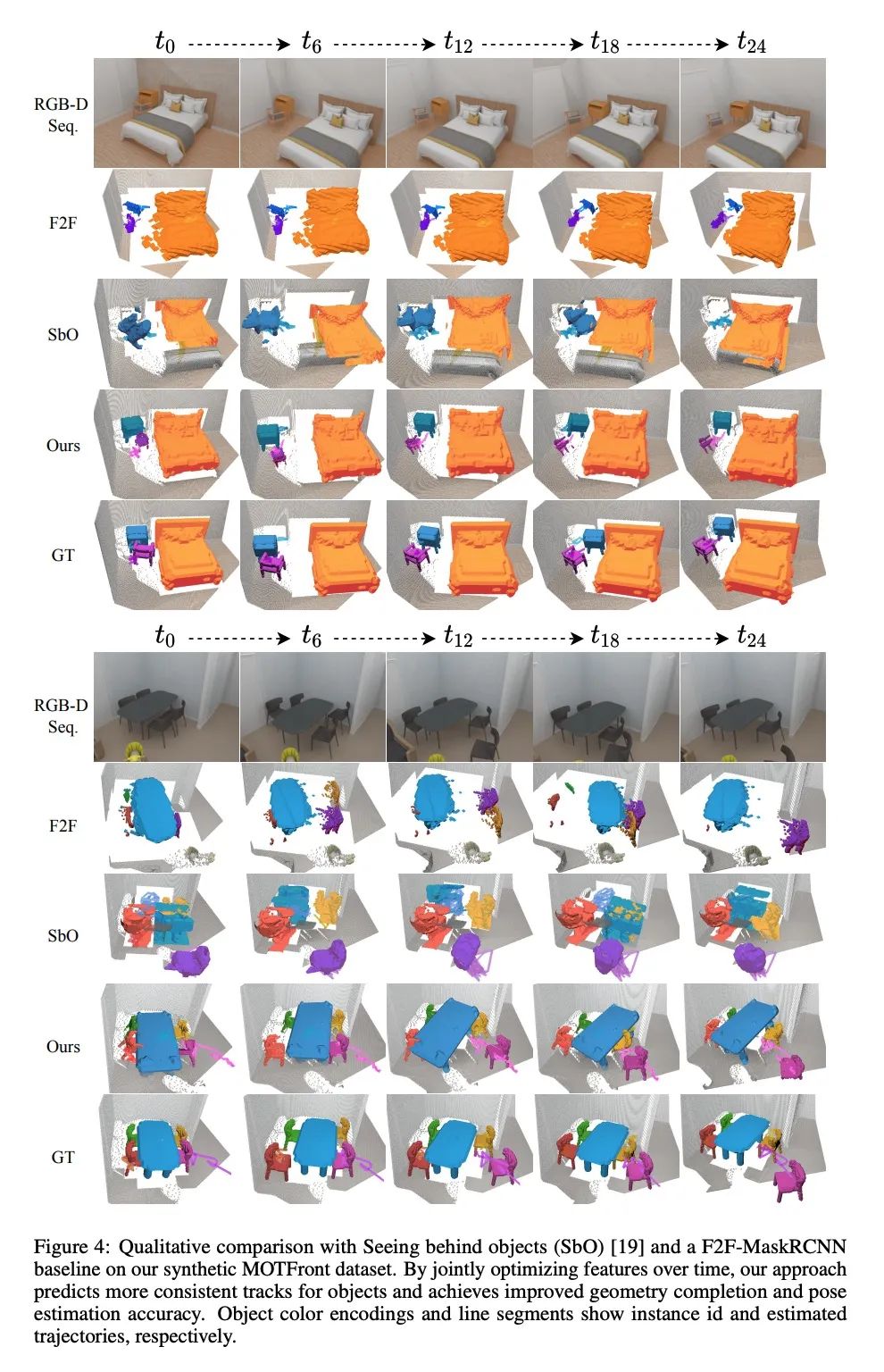
[CV] 3D Multi-Object Tracking with Differentiable Pose Estimation
基于可微姿态估计的3D多目标跟踪
D Schmauser, Z Qiu, N Müller, M Nießner
[Technical University of Munich]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.13785


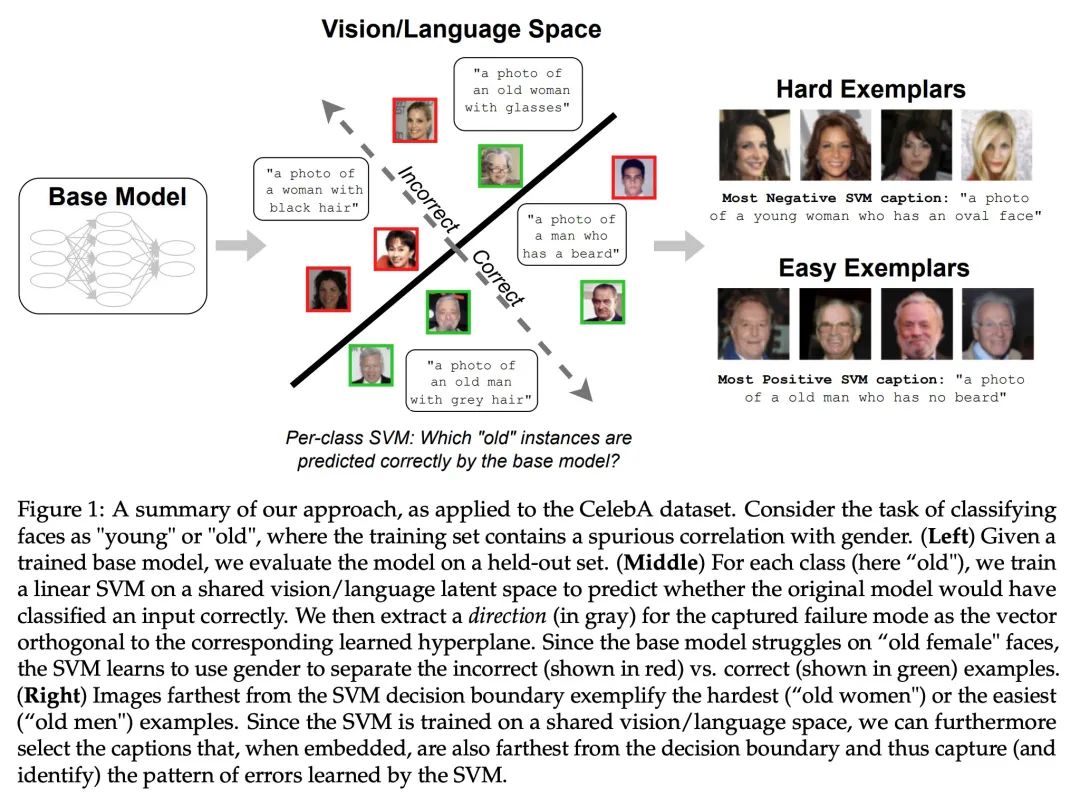
[LG] Distilling Model Failures as Directions in Latent Space
提炼模型失效模式作为潜空间方向
S Jain, H Lawrence, A Moitra, A Madry
[MIT]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.14754



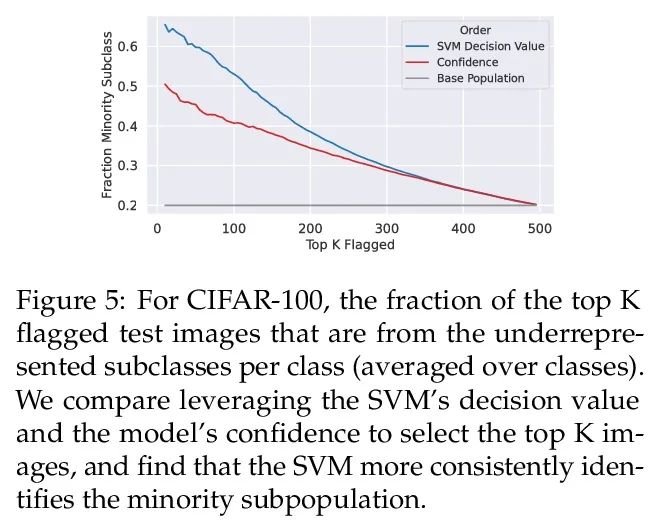
[CL] Factuality Enhanced Language Models for Open-Ended Text Generation
面向开放式文本生成的事实性增强语言模型
N Lee, W Ping, P Xu, M Patwary, M Shoeybi, B Catanzaro
[Hong Kong University of Science and Technology & NVIDIA]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.04624

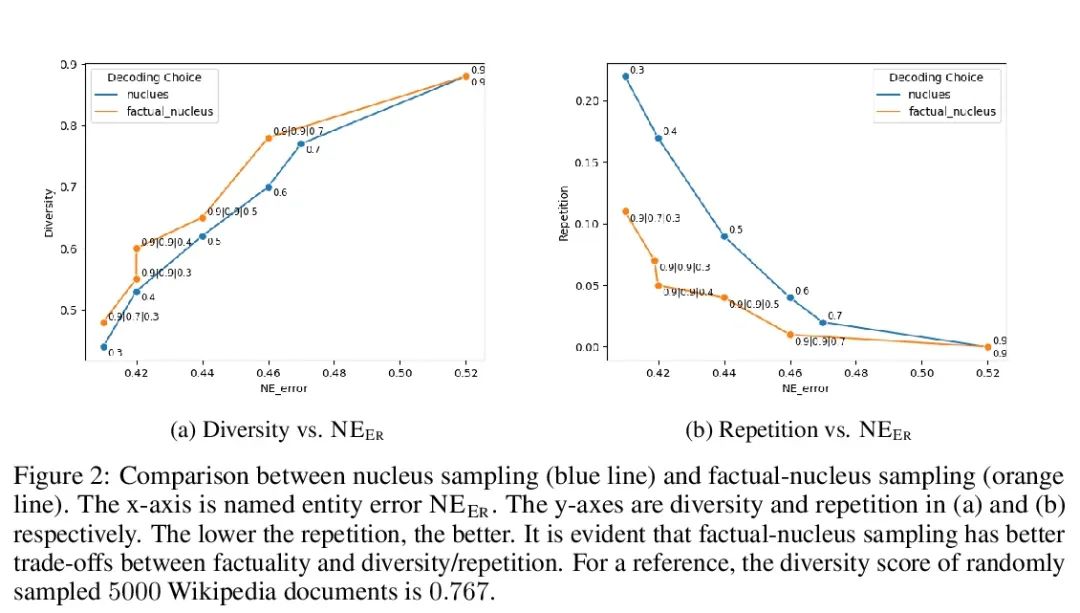

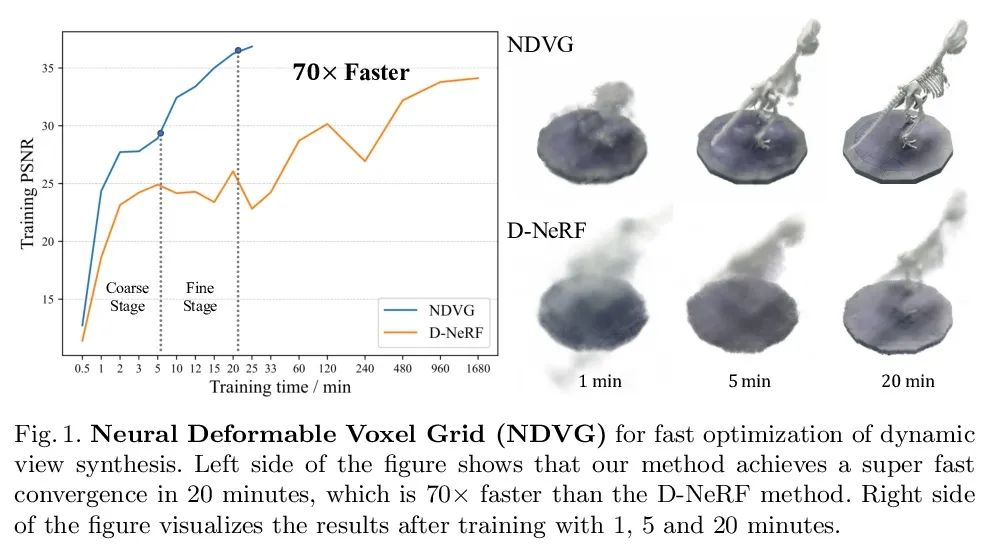
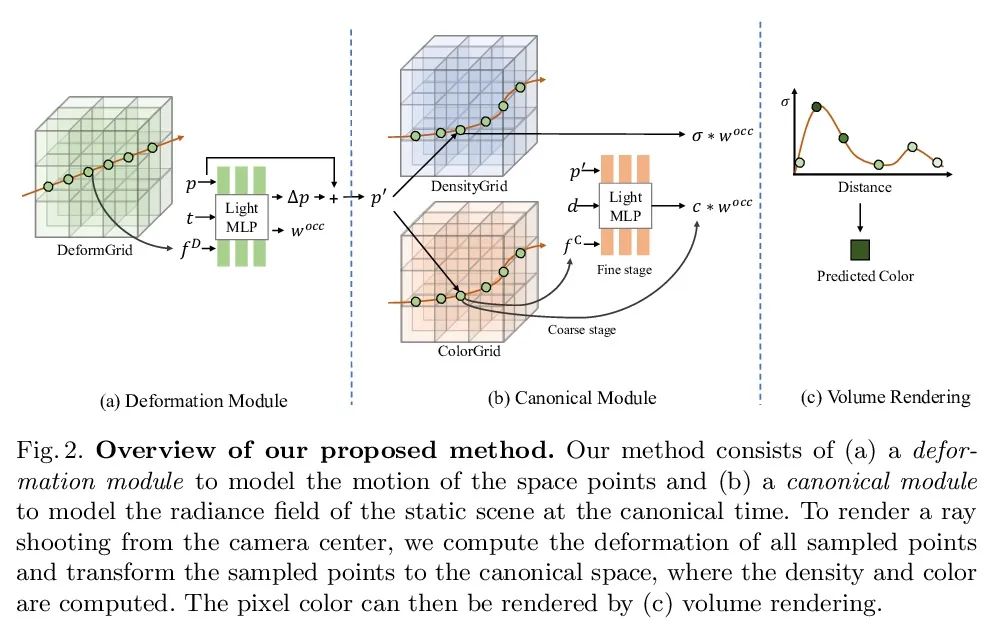
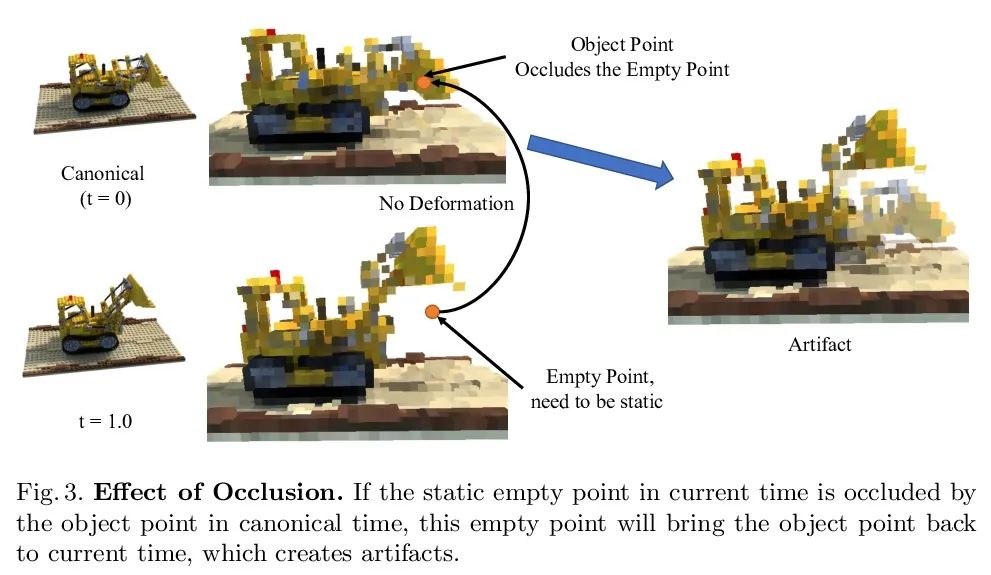
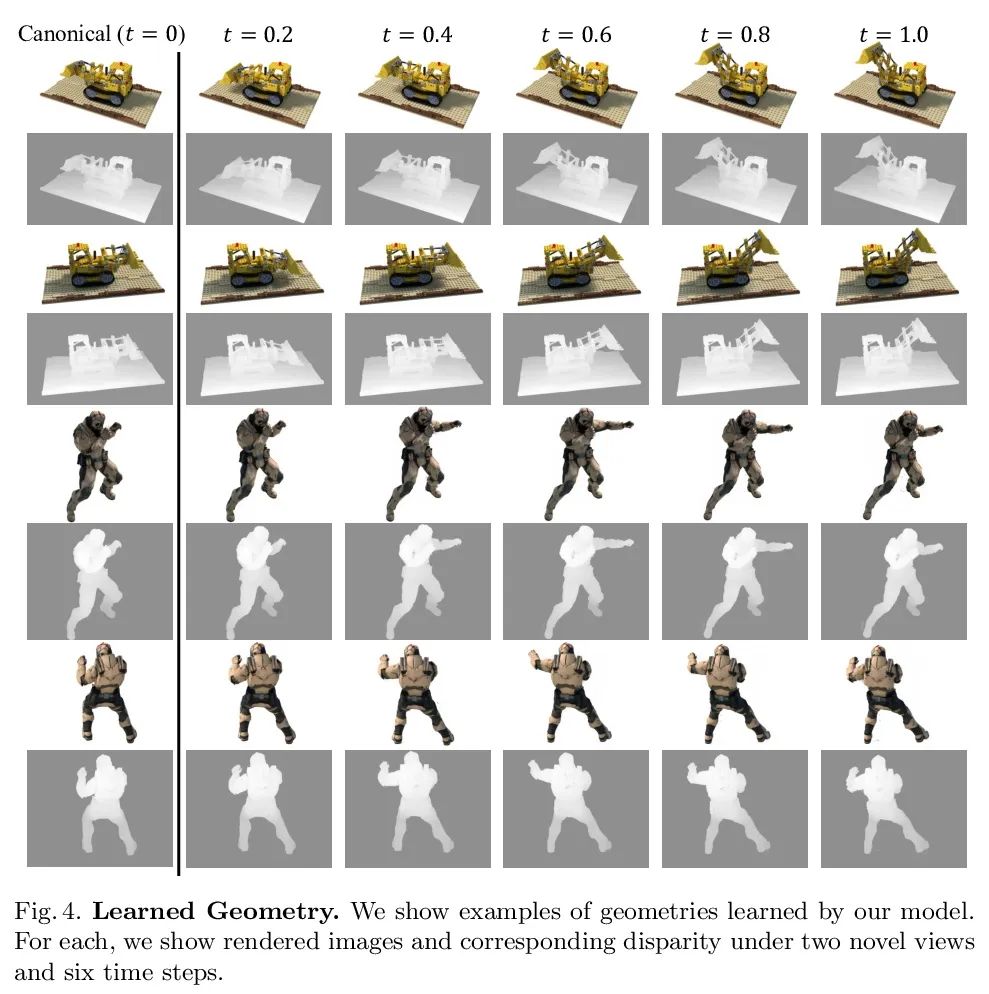
[CV] Neural Deformable Voxel Grid for Fast Optimization of Dynamic View Synthesis
面向动态视图合成快速优化的神经可变形体素网格
X Guo, G Chen, Y Dai, X Ye, J Sun, X Tan, E Ding
[Northwestern Polytechnical University & The Chinese University of Hong Kong & Baidu]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.07698